New Publication in ES&T
Reaction of Chlorine Dioxide with Saturated Nitrogen-Containing Heterocycles and Comparison with the Micropollutant Behavior in a Real Water Matrix
2022/08/18
Mohammad Sajjad Abdighahroudi, Xenia A. M. Mutke, Mischa Jütte, Katharina Klein, Torsten C. Schmidt, and Holger V. Lutze
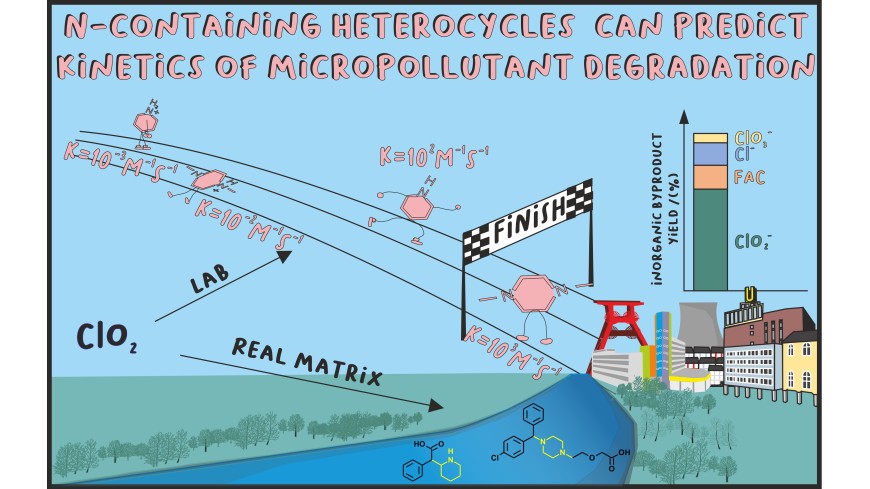
Chlorine dioxide (ClO2) is a very selective oxidant that reacts with electron-rich moieties such as activated amines and thus can degrade specific N-containing micropollutants. N-containing heterocycles (NCHs) are among the most frequent moieties of pharmaceuticals. In this study, the reactions of ClO2 with ritalinic acid and cetirizine, two abundant micropollutants, and model compounds representing their NCH moiety were investigated. The pH-dependent apparent reaction rates of all NCHs with ClO2 were measured and modeled. This model showed that neutral amines are the most important species having reaction rates between 800 and 3200 M–1 s–1, while cationic amines are not reactive. Ritalinic acid, cetirizine, and their representative model compounds showed a high stoichiometric ratio of ≈5 moles ClO2 consumption per degraded ritalinic acid and ≈4 moles ClO2 consumption per degraded cetirizine, respectively. Investigation of chlorine-containing byproducts of ClO2 showed that all investigated NCHs mostly react by electron transfer and form above 80% chlorite. The reactions of the model compounds were well comparable with cetirizine and ritalinic acid, indicating that the model compounds indeed represented the reaction centers of cetirizine and ritalinic acid. Using the calculated apparent reaction rate constants, micropollutant degradation during ClO2 treatment of surface water was predicted for ritalinic acid and cetirizine with −8 to −15% and 13 to −22% error, respectively. The results indicate that in ClO2-based treatment, piperidine-containing micropollutants such as ritalinic acid can be considered not degradable, while piperazine-containing compounds such as cetirizine can be moderately degraded. This shows that NCH model compounds could be used to predict micropollutant degradation.
